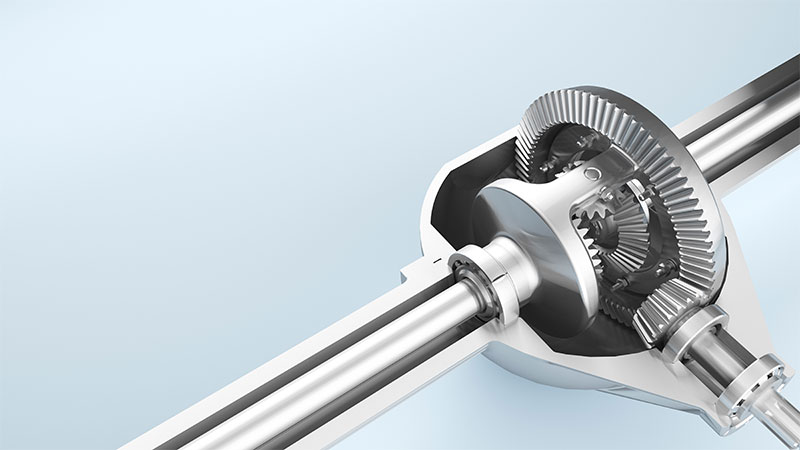
Many people hear the word differential and think of 4WD/AWD vehicles, but the fact is there is a car differential on many different types of cars & trucks. Knowing how it works & the warning signs of a failing car differential can save you a lot of money on additional repairs by replacing it before it fails.
In this My Auto Store blog post we will tell you how the car differential works, the different types of differentials in vehicles, &. how to know when one is failing. So if you’re suspecting this may be your problem with your vehicle, then keep reading to find out more.
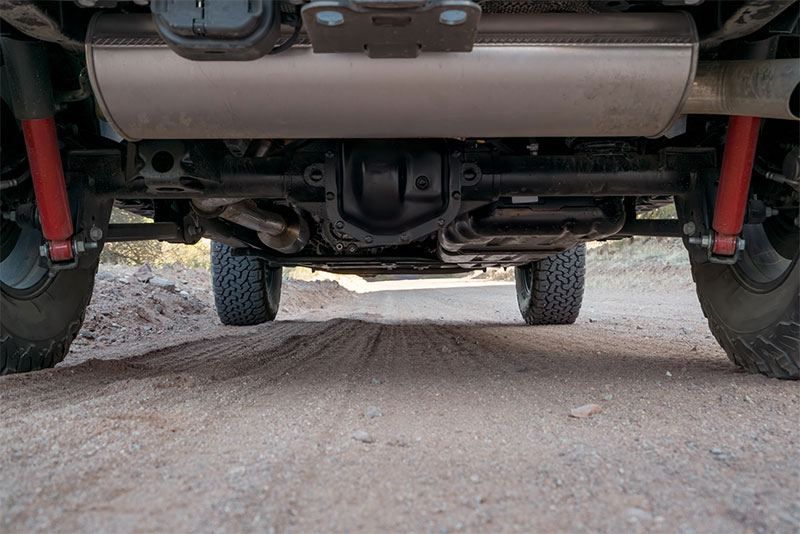

Differentials Role In The Drivetrain
Differentials receive power from the driveshaft and deliver it to the wheels. A differential consists of many different components. The driveshaft typically connects to the pinion shaft/gear through a universal joint, the pinion gear spins a much larger ring gear, and attached to the ring gear are two parallel spider gears that then attach to side gears that are at the end of the two axles.
The axles then attach to your hub, which is the piece that connects to your wheel. All of these things together allow the wheels to spin at different speeds and are pivotal in turning. When you make a turn, one of the wheels on your differential must turn sharper than the other and therefore it is necessary the differential has the ability to allow the wheels to spin at different speeds.
Types Of Differentials
- Open Differentials: There are open differentials, which are the most common type coming from the manufacturer. An open differential splits the torque equally to both wheels. When a tire loses traction, less torque is applied to both wheels until traction is established again. These are good for everyday vehicles because it allows the wheels to spin at different speeds and helps in ensuring smooth turning.
- Limited Slip Differentials: A limited-slip differential functions primarily as an open differential, the only difference is it has an additional component, being a set of clutch plates, a more complex differential gear train or a special viscous fluid. One of these three components senses when a wheel loses traction and will send torque to both wheels instead of one to regain traction.
- Locking Differentials: A locking differential is similar to both of these previous differentials, the only difference being that the user is able to select whether the drive train is open or locked. This feature is great to turn on when you are in situations where you need more traction like in sand, snow, dirt, or mud but can be a problem when on a hard surface. When the vehicle is locked and goes into a turn both wheels are trying to spin at the exact same speed, this is impossible because one of the wheels is taking a shorter path. This complication can lead to things such as axles snapping because the grip friction between the tire and the pavement won’t allow the wheels to spin at different speeds and the torque is then transferred to the weakest components, typically the axle.
- Torque Vectoring Differentials: The last type of differential is the torque-vectoring differential. This is the most complex form of differential and it consists of extra gear trains and a lot of sensors and computers that control precisely how much torque is given to each wheel. Whereas in other vehicles, there’s only a mechanical aspect as to what controls the torque change. These are typically found in high-end luxury sports sedans or crossovers such as Audi, Lexus, and BMW. These are not used in most vehicles because of the cost to produce them and the complexity of the system itself.
Gear Ratio
A differential gear ratio is the difference between the number of teeth on the ring gear and the pinion gear. If your ring gear has 41 teeth and your pinion gear has 11 teeth (pinion gears are always smaller) then your gear ratio would be 41/11 or 3.73. This means that the driveshaft (remember the driveshaft is directly connected to the pinion gear via u-joint) would have to spin 3.73 revolutions for the wheels to turn 1 revolution.
This seemingly complex system allows manufacturers to control torque/acceleration and top speed capabilities based on the car’s functional purposes. The higher the gear ratio (e.g. 5.13), the more the driveshafts have to spin to turn the wheels. This is great for vehicles that need more torque such as trucks because it raises their towing capacity.
A higher gear ratio typically consists of parts made from more durable materials as well, which helps ensure keeping work vehicles on the road. A lower gear ratio (e.g. 3.73) makes the driveshaft have to spin less to achieve more rotations at the wheel, this is good for smaller cars that don’t need as much torque or power distributed to the wheels. These cars are more fuel efficient and better for highway use.
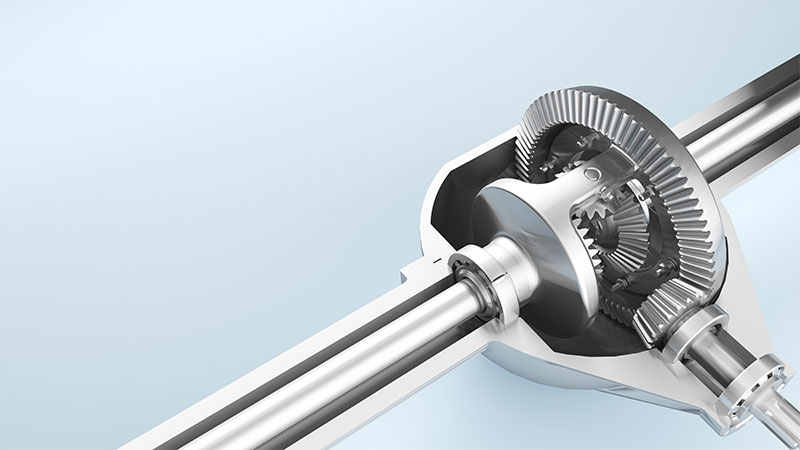
Difference Between Transfer Case & Differential
Transfer cases allow power to be distributed to both the front and rear wheels and are only found in 4×4 and AWD vehicles. The transfer case gets power directly from the transmission and delivers it to the rear wheels or in some vehicles, it delivers power to both the front and rear wheels.
Distributing power to the differentials is a huge task and takes meticulous maintenance and servicing to ensure no fatal flaws when you are out on the road. Transfer cases in AWD cars are typically automatically controlling all 4 wheels and usually have a button that will “lock” all 4 wheels for situations when you are moving slowly and need more traction, like snow or mud.
4×4 vehicles typically have either manual transfer case selection, shifter, or electrical selection button or switch. These selectors allow the vehicle to be driven primarily in 2WD, with the option for 4×4 high and low gears depending on the application.
The function of Transfer Cases & Differentials
Transfer cases and differentials have similar functions, they both take power from the transmission and reroute it. A transfer case takes power directly from the transmission and delivers it to both the front and rear differentials through driveshafts.
A differential either receives its power from the transmission or the transfer case via driveshafts and delivers it to the wheels. While they have similar gear trains a transfer case never has to deliver power to the wheels, so it does not have anything more than gearing components inside it. Since differentials have to deliver power to the wheels they consist of more components such as axles, brakes, and suspension components.
The Axle’s Role In Differential & Drivetrain
An axle connects directly to the ring gear through a series of wheel bearings and delivers power from the ring gear to the hub which attaches to your wheels and spins them. They can consist of one solid piece or multiple smaller pieces.
If you want to learn a little more about the role an axle plays in the drivetrain check out An Axle’s Role In The Drivetrain.
Maintenance
Maintaining your differential and knowing the signs of a failing differential is crucial in keeping your car on the road. The fluid inside the differential is meant to be replaced generally every 30,000-60,000 miles, but every manufacturer recommends something different.
To be sure of how often your fluid should be replaced, what kind of fluid to use and the quantity, please refer to the owner’s manual. Another crucial component that needs to be serviced regularly is your braking system. Pads should generally be replaced every 10,000-20,000 miles and rotors every 50,000-70,000.
If you want to learn more about when it is time to maintain your brakes or rotors, check out “Does Your Car Need New Brakes?”
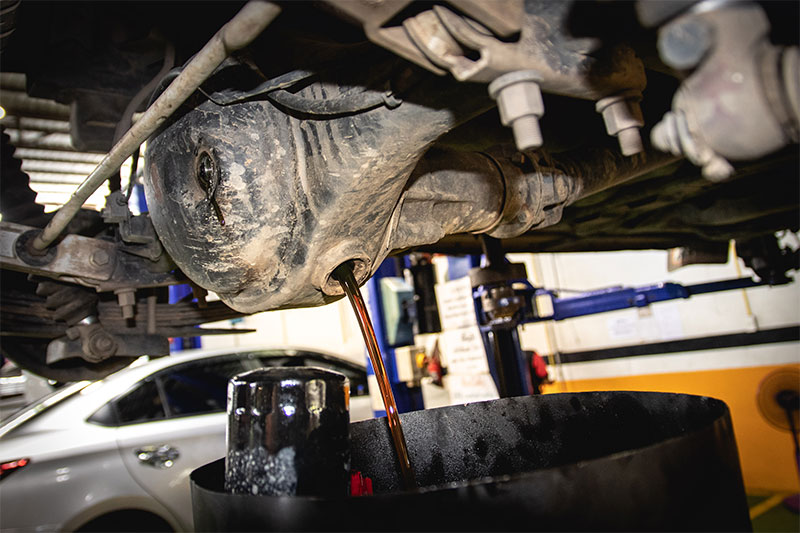

Bad Differential Symptoms
Other than regular fluid changes, careful inspection of the differential should also be done on a regular basis. Components such as wheel bearings, universal joints, internal gears, and axles all tend to make noises when they are starting to fail.
If you hear any kind of metal-on-metal grinding, popping, wheeling, or clicking coming from the front or rear of your vehicle it is important that you have it looked at immediately! More times than not, a part that is starting to fail, rather than one that has already failed, is cheaper to replace.
Another way to inspect your differential for signs of failing components is to visually inspect the pieces. If you see damp or wet spots around the differential in any place this could be a sign that one of the many seals that keep the fluid inside the differential is failing.
These seals play a very important role in keeping the differential fluid inside the differential allowing the fluid to keep the metal components from getting too hot. As well as keeping fluid in these seals, also keeps things such as dirt, sand, and water out.
Having sand or dirt enter your differential is very bad as it creates more friction between the moving gears and leads to catastrophic failure. While looking for fluid leaks, be sure to also be on the lookout for anything that looks out of place, many times components that are broken or on the way out will look out of line.
What Happens When My Differential Fails?
If your differential begins to or completely fails, don’t worry! You do have options. First, you could bring it to a shop, and have them repair or replace the differential. This would be the most expensive option, it really does depend on if they are repairing or replacing it.
Differential repairs can be costly when things like gears need to be replaced but may not be as harsh when it is something like seals that need to be replaced. Either way, the labor will cost a pretty penny alone.
On the other hand, they may replace the entire differential completely and this is another item on the bill they can upcharge. This is because they usually buy parts for a cheaper price and then mark them up on your bill. Why? Because they can!
Depending on what is wrong with the differential you can try to fix it yourself or do a differential rebuild, which is your second option. This can be as simple as needing a differential fluid change and as complicated as needing new gears. Even if you do fix the seals and replace the gears, this takes a lot of time and this is not a guarantee that it won’t begin to fail again later on down the line.
Your third option is probably the cheapest and easiest option in the long run. Just buy a used one for your exact make and model from a used auto parts supplier like My Auto Store. Then you can replace it yourself or have a trusted mechanic replace it for you. We like to call these types of mechanics “backyard” mechanics and you can learn more about why they are becoming more popular by reading “Why Auto Repair Costs Will Keep Rising”.
Why Buy a Used Auto Part Over a New Replacement Part
You don’t want to buy a brand new differential for a vehicle that is halfway or more through its life, that would be a waste of money. This part does not tend to break during the car’s lifetime unless it is not maintained properly or it is faulty. Instead, buy a used one that is not failing and get it replaced! This will save you the time of trying to repair the complex components of the differential and reduce the cost caused by the mechanic up charging you!
Now, you may be wondering, where can I find a used differential without paying an arm and a leg? We recommend you go straight to the source and cut out any middlemen who throw in an extra charge just for being the middleman! The source you need is My Auto Store.
We not only have one to match your exact make and model but we have fair prices that won’t break your bank. Along with that, we offer a six-month warranty on all our car parts and offer free shipping throughout the entire continental United States!
You can browse our used auto parts inventory online now or give us a call at 1-866-513-3788 and we can help get your 4WD/AWD vehicle back on all fours in no time!